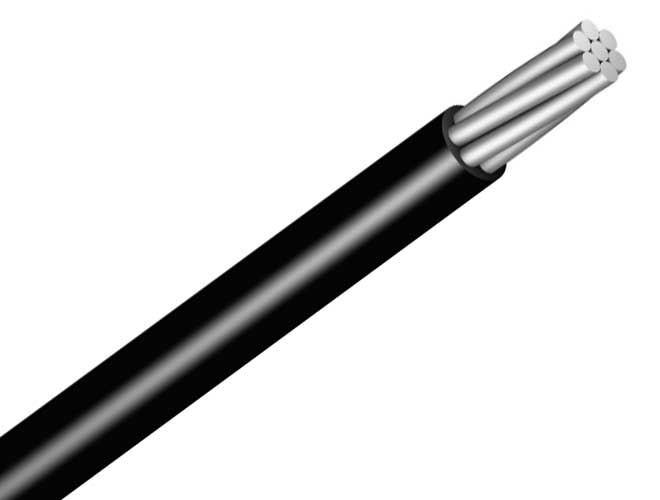
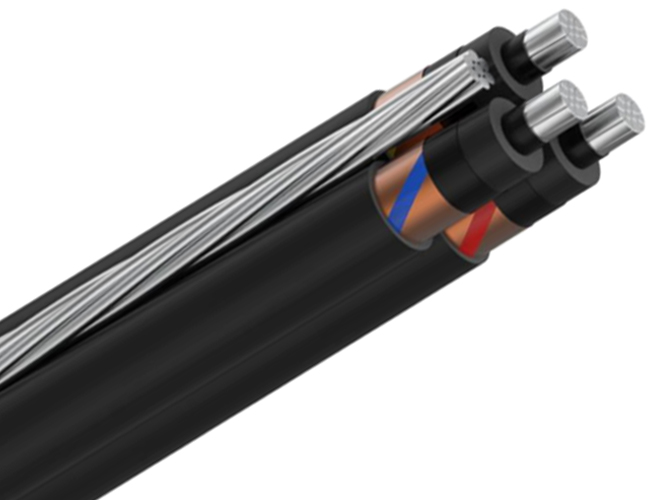
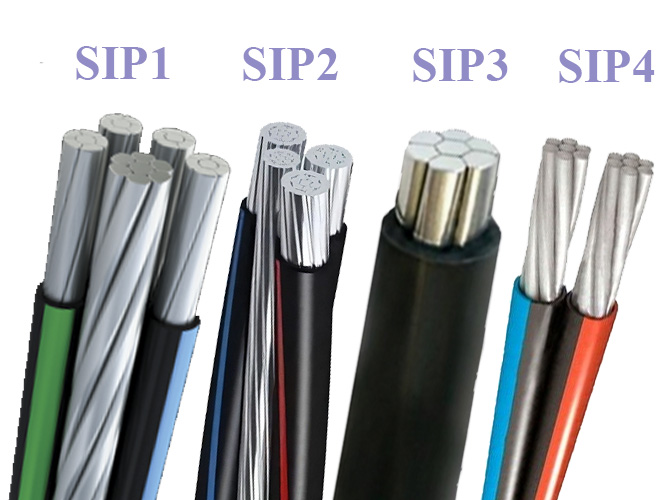
ADDRESS :
Factory :No.33 Zhengzhou City, Henan Province,China
WHATSAPP/MOBILE/WECHAT:
+86186 2554 1622
Email :
info@cable-uni.com
products
fast LINKS
message
Subscribe to our email newsletter to receive
useful articles and special offers.