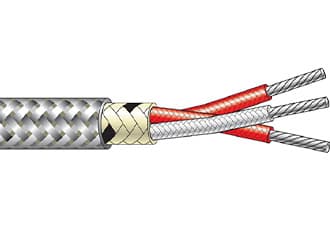
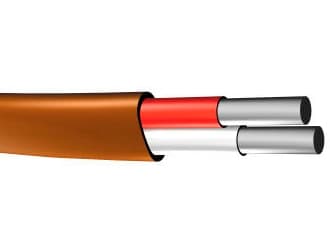
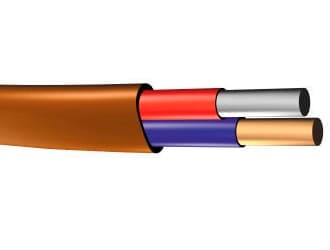
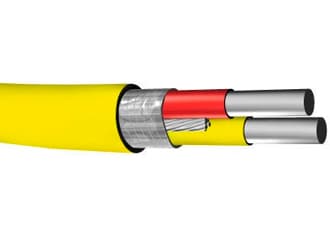
Thermocouple extension and compensating cables
QZ Cable's Thermocouple Compensating & extension cables products comply with International Standards, including standards IEC 60584-3, British standards BS4937, German standard DIN 43710, and US standard ANSI MC 96.1. QZ Cable offers a full line of thermocouple cable & wire with standard limits of error & special limits of error. Thermocouple alloy wires are available in solid or stranded configurations. We offer a wide variety of insulating, shielding, and jacketing options for our single-pair thermocouple wire & our multipair thermocouple extension cables.
What is the application of extension and compensating cables?
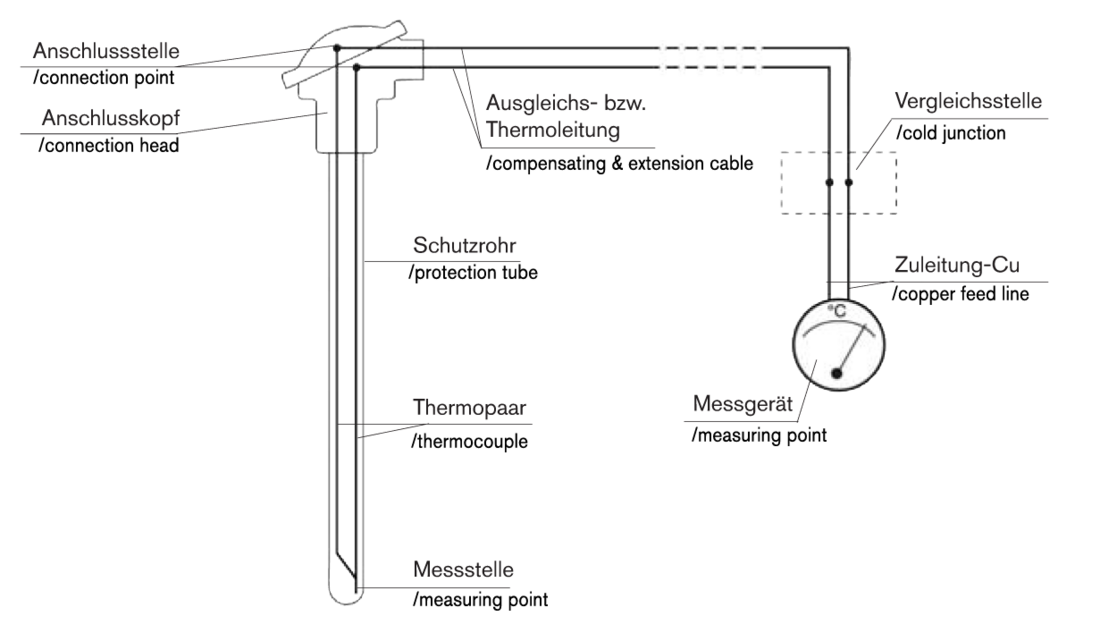
The value of the electromotive force (EMF) produced by the thermocouple is determined by the difference between the measuring temperature and the so-called free ends of the thermocouple which are mounted in the connection head. As the connection head is usually relatively close to the measuring point, it is frequently exposed to temperature fluctuations. For this reason, a connection cable with the same thermoelectric properties as the thermocouple is used between the thermocouple and the cold junction. This link-up provides the compensating/extension cable.
| Code |
+ve Leg |
-ve Leg |
EMF at 100° C in milli volt ref. Jn. at 0° C |
Recommended working temp. in Celsius |
Remarks |
| K |
Chromel (Alloy of Chromium & Nickel) |
Alumel (Alloy of Aluminium & Nickel) |
4.09 |
0°C to 1100° C |
Most Commonly used |
| T |
Copper |
Contrantan (Alloy of Copper & Nickel) |
4.28 |
-185 C to 300° C |
For low temp. & cryogenic applications |
| J |
Iron |
Constantan |
5.27 |
20° C to 700° C |
Used in reducing Atmosphere |
| E |
Chromel |
Constantan |
6.32 |
0° C to 800° C |
Highest EMF output |
| R |
Platinum + 13% Rhodium |
Platinum |
0.647 |
0° C to 1600° C |
Very high temp. measurements |
| S |
Platinum + 10% Rhodium |
Platinum |
0.645 |
0° C to 1500° C |
Very high temp. measurements |
| B |
Platinum + 30% Rhodium |
Platinum + 6% Rhodium |
0.033 |
100° C to 1500° C |
Mainly used in glass industry |
What is the material difference between a thermocouple extension cable and a thermocouple compensation cable?
We differentiate between thermocouple cable and compensating cable. Cables made of original materials are called extension or thermocouple cables, whereas conductor materials made of substitutes are known as compensating cables.
Compensating cables
The compensating wires and strands are composed of alloys that do not have to be identical to the corresponding thermocouple. Substitute material means that the thermo-electric characteristics in the allowed temperature range (usually 0 up to +200 °C) for the compensating cable must be the same as those of the corresponding thermocouple. They are identified with the letter ”C“ adapted to DIN IEC 584. The ”C” appears behind the code letter identifying the thermocouple, for example,” KC”.
Thermocouple Extension Cables
Extension cables are made of conductors with identical nominal structures to the corresponding thermocouple. They are identified with the letter ”X” adapted to DIN IEC 584, which appears behind the code letter identifying the thermocouple, for example,” JX”. They are normally tested within a temperature range of 0 up to +200°C.
Thermocouple Cables
Thermocouple cables consist of the same element material as the thermocouple and are tested for the same temperatures. These special cables are manufactured on customer request. PVC, fiberglass, and tex-insulated or sheathed compensating and extension cables are not suitable for outdoor use. Exception: PVC-sheathed solid conductors can be used for underground laying.
QZ Cable offers Thermocouple Compensating & extension cables products including:
| Standard |
Thermocouple Compensating & extension cables(Colour code and temperature range for compensating and extension cables) |
| IEC 60584-3 |
PVC insulated compensating and extension cables, up to 70°C
Silicone insulated compensating and extension cables, up to +180°C
Fibre-glass insulated compensating and extension cables up to +180°C/+200°C
FEP insulated compensating & thermocouple extension wires up to +180°C
PFA insulated extension cables up to +250°C
FEP, PFA, or Silicone insulated connection cables +180℃ /+250℃
PTFE insulated, PFA sheathed unshielded/shielded thermocouple extension cables
PT100, ETFE insulated, ETFE sheathed, shielded resistance measurement cables,600/1000 V AC |
| ANSI MC 96.1 |
Low Temperature Insulation Thermocouple(PVC - 105ºC | Nylon 121ºC):
Unshielded PVC Insulated Jacketed Parallel Pair Thermocouple Cable
Shielded PVC Insulated and Jacketed Twisted Pair Thermocouple Cable
Type EX Multi-pair Overall Shield PVC Insulated and Jacketed Thermocouple Extension Cable
Type SX Multi-pair Individual and Overall Shield PVC Insulated and Jacketed Thermocouple Extension Cable
Unshielded Nylon Insulated and Jacketed Parallel Pair Thermocouple Cable
High Temperature Insulation Thermocouple(FEP - 200ºC | PTFE - 260ºC | PFA - 260ºC):
Shielded-PFA Insulated and Jacketed Twisted Pair Thermocouple Cable
Unshielded PFA Insulated and Jacketed Parallel Pair Thermocouple Cable
Twisted Pair Thermocouple Cable Shielded PFA Insulated and Jacketed
Unshielded PTFE Tape Insulated and Jacketed Parallel Pair Thermocouple Cable
Shielded-FEP Insulated and Jacketed Twisted Pair Thermocouple Cable
Unshielded FEP Insulated and Jacketed Parallel Pair Thermocouple Cable
Unshielded-FEP Insulated and Unjacketed Twisted Pair Thermocouple Cable |
| BS4937 |
Armoured/Non-Armoured Compensating & Thermocouple Cable |
| CSA C22.2 |
CSA ACIC Armoured Thermocouple Extension | Pairs (300V)
CSA Unarmoured Tray Thermocouple Extension | Pairs (300V) |