Applications of OPGW:
Power Utilities:
Widely used by power utilities to provide a reliable communication link for monitoring and controlling the power grid.
Enables real-time data transmission for smart grid applications, fault detection, and system management.
Telecommunications:
Can be leased to telecom companies to provide backbone communication links, offering an additional revenue stream for power utilities.
OPGW cable components
1.Steel or aluminum central tube
2.Optical Fiber
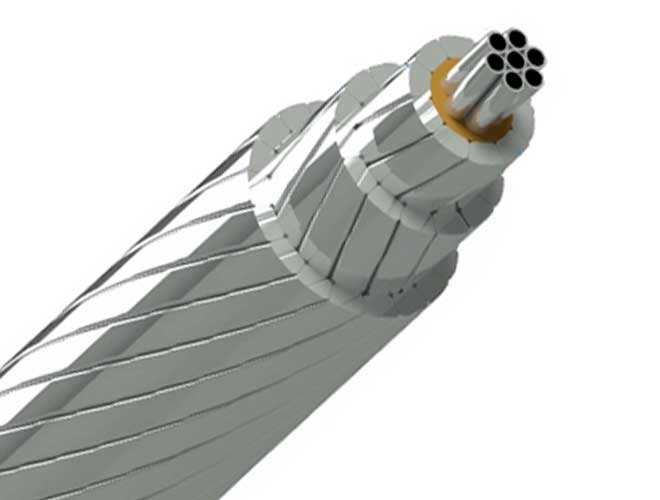
3.Cable sheath that consists of one or more layers of sheath wires
OPGW fiber optic cable types
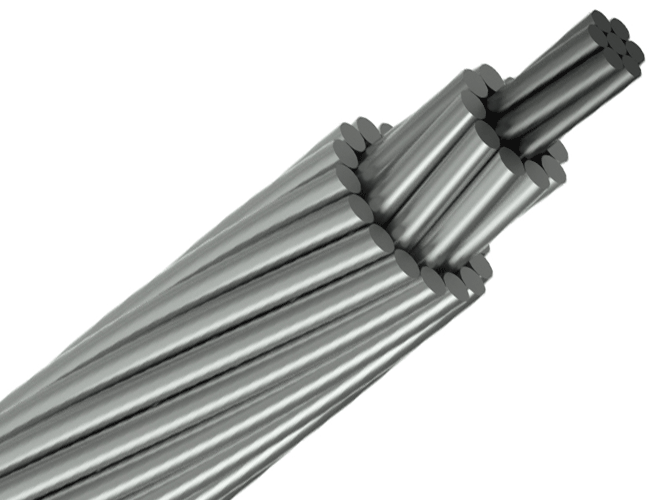
OPGW cables are used in the highest point of the overhead transmission lines' towers. Optical Cable is mainly used in communication line of newly constructed high voltage transmit electricity system with 35 KV or above, or replacement of existing ground wire of previous overhead high voltage transmit electricity system. OPGW cable consists of one or more aluminum or steel tubes containing a certain number of optical fibers and aluminum-coated steel wires used in the first layer of the cable and in the other layers of aluminum, steel, aluminum alloy wires or a combination of Them, that are used based on the required electrical and mechanical specifications. The number of optical fibers used in the tubes varies and depending on the need and type of cable, one fiber can be used and reach 12, 24, 48 numbers or even higher.
In the design and production of OPGW cables, single-mode and multi-mode fibers can be used.
Single-mode fibers are used for distances of more than one kilometer with high bandwidth and Multi-mode fibers are used for distances of less than one kilometer with lower bandwidth.
Conductor opgw are similar to ACSR conductors' appearance or shield wires, and have replaced guard wires in older transmission and distribution lines; In the design of new transmission lines, Cables De Guarda OPGW are also used as products with both protective and transmitter applications.
Power Utilities:
Widely used by power utilities to provide a reliable communication link for monitoring and controlling the power grid.
Enables real-time data transmission for smart grid applications, fault detection, and system management.
Telecommunications:
Can be leased to telecom companies to provide backbone communication links, offering an additional revenue stream for power utilities.
OPGW cable components
1.Steel or aluminum central tube
2.Optical Fiber
3.Cable sheath that consists of one or more layers of sheath wires
OPGW fiber optic cable types
| 1. Central Stainless Steel Loose Tube OPGW Wire (Center SST OPGW Wire Cable) | 2. Aluminium Covered/Clad PBT Tube OPGW Wire |
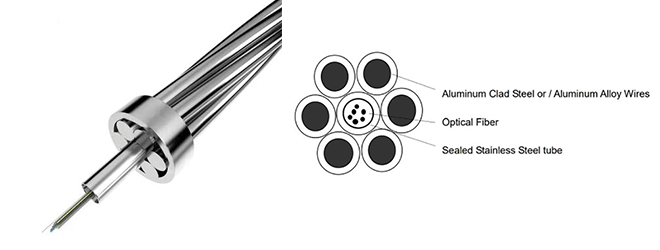 |
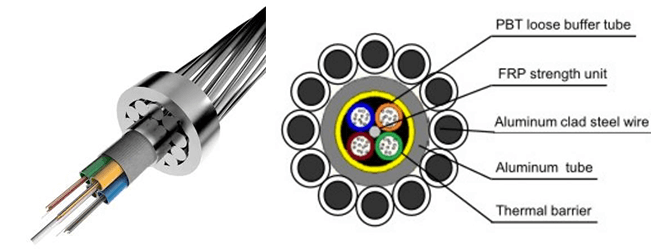 |
| 3. Central/Center Aluminium-Clad Stainless Steel Tube OPGW Wire(AL Clad SST OPGW Wire Cable) | 4. Stranded Stainless Steel Tube OPGW Wire(Stranding SST OPGW Wire Cable) |
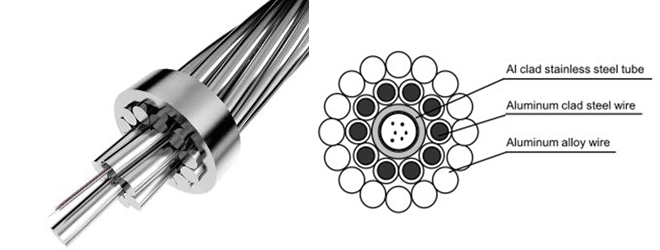 |
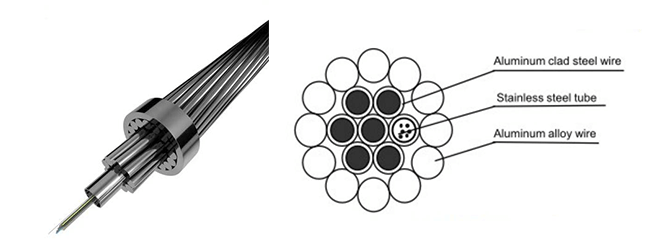 |
OPGW cables are used in the highest point of the overhead transmission lines' towers. Optical Cable is mainly used in communication line of newly constructed high voltage transmit electricity system with 35 KV or above, or replacement of existing ground wire of previous overhead high voltage transmit electricity system. OPGW cable consists of one or more aluminum or steel tubes containing a certain number of optical fibers and aluminum-coated steel wires used in the first layer of the cable and in the other layers of aluminum, steel, aluminum alloy wires or a combination of Them, that are used based on the required electrical and mechanical specifications. The number of optical fibers used in the tubes varies and depending on the need and type of cable, one fiber can be used and reach 12, 24, 48 numbers or even higher.
In the design and production of OPGW cables, single-mode and multi-mode fibers can be used.
Single-mode fibers are used for distances of more than one kilometer with high bandwidth and Multi-mode fibers are used for distances of less than one kilometer with lower bandwidth.
Conductor opgw are similar to ACSR conductors' appearance or shield wires, and have replaced guard wires in older transmission and distribution lines; In the design of new transmission lines, Cables De Guarda OPGW are also used as products with both protective and transmitter applications.
| Structure parameters | OPGW Technical parameter table | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S/N | Product code | Structure form of the optical cable | The largest core number of the fiber (core) | Sectional area of aluminum clad steel (mnr) | Outer diameter (mm) | Mass of unit length (kg/km) | Rated breaking force (kN) | 20X DC resistance (Q/km) | 40-2001 permitted short- circuit current capacity |
| 1 | OPGW-24B1-40(51;9) | 6/3.0/20ASoptical unit1/3.0 | 24 | ≈40 | 9.0 | 304 | 51 | 2.10 | 9 |
| 2 | OPGW-36B1 -50 (58; 11.5) | 6/3.2/20ASoptical unit1/3.2 | 36 | ≈50 | 9.6 | 345 | 58 | 1.82 | 11.5 |
| 3 | OPGW-36B1-60 (70;17.5) | 6/3.6/20ASoptical unit .3.6 | 36 | ≈60 | 10.8 | 432 | 70 | 1.41 | 17.5 |
| 4 | OPGW-48B1-70 (77;24) | 6/3.8/20ASoptical unit Z3.8 | 48 | ≈70 | 11.4 | 475 | 77 | 1.30 | 24 |
| 5 | OPGW-48B-70 (42;38) | 6/3.8/40ASoptical unit/3.8 | 48 | ≈70 | 11.4 | 340 | 42 | 0.70 | 38 |
| 6 | OPGW-48B1-80 (86;29.2) | 6/4.1/20ASoptical unit1/4.1 | 48 | ≈80 | 12.3 | 558 | 86 | 1.09 | 29.2 |
| 7 | OPGW-48B1-80 (49;45.0) | 6/4.1/40ASoptical unit1/4.1 | 48 | ≈80 | 12.3 | 401 | 49 | 0.55 | 45 |
| 8 | OPGW-24B1-90 (109;35.5) | 1 /2.5/20AS+5/2.5/20AS+12/2.5/20AS.optical unit1/2.5 | 24 | ≈90 | 12.5 | 606 | 109 | 0.98 | 35.5 |
| 9 | OPGW-48B1-90 (112;45) | 1/2.6/20AS+4/2.5/20AS+11/2.8/20AS.optical unit2/2.5 | 48 | ≈90 | 13.2 | 641 | 112 | 0.98 | 45 |
| 10 | OPGW-24B1-100 (118;50) | 1/2.6/20AS+5/2.5/20AS+11/2.8/20AS.optical unit/2.5 | 24 | ≈100 | 13.2 | 674 | 118 | 0.93 | 50 |
| 11 | OPGW-48B1-100 (121;45) | 1 Z2.5/20AS+4/2.4/20AS+10/3.1/20AS.optical unit2/2.4 | 48 | ≈100 | 13.5 | 688 | 121 | 0.88 | 45 |
| 12 | OPGW-24B1-110 (133;63) | 1 /2.6/20AS+5/2.5/20AS+10/3.2/20AS.optical unit1/2.5 | 24 | ≈110 | 14.0 | 760 | 133 | 0.83 | 63 |
| 13 | OPGW-48B1-110(133;58.2) | 1/2.6/20AS+4/2.6/20AS+10/3.3/20AS.optical unit2/2.6 | 48 | ≈110 | 14.4 | 783 | 133 | 0.77 | 58.2 |
| 14 | OPGW-36B1 -120(145;73) | 1/3.0/20AS+5/2.9/20AS+12/2.9/20AS.optical unit1/2.8 | 36 | ≈120 | 14.6 | 820 | 145 | 0.77 | 73 |
| 15 | OPGW-36B1 -120(74;110) | 1/3.0/40AS+5/2.9/40AS+12/2.9/40 AS.optical unit/2.8 | 36 | ≈120 | 14.6 | 582 | 74 | 0.42 | 110 |
| 16 | OPGW-72B1 -120(147;76) | 1/3.0/20AS+4/3.0/20AS+12/3.0/20AS.optical unit2/2.9 | 72 | ≈1120 | 15.2 | 832 | 147 | 0.76 | 76 |
| 17 | OPGW-36B1 -130(155;85) | 1/3.2/20AS+5/3/0/20AS+12/3.0/20AS.optical unit1/2.9 | 36 | ≈130 | 15.2 | 879 | 155 | 0.72 | 85 |
| 18 | OPGW-36B1 -130(79; 137) | 1/3.2/40AS+5/3.0/40AS+12/3.0/40 AS.optical unit/2.9 | 36 | ≈1130 | 15.2 | 624 | 79 | 0.40 | 137 |
| 19 | OPGW-36B1-140(175; 100) | 1/3.3/20AS+5/3.2/20AS+12/3.2/20AS.optical unit1/3.1 | 36 | ≈1140 | 16.1 | 995 | 175 | 0.65 | 100 |
| 20 | OPGW-48B1-150(182; 123) | 1/3.4/20AS+5/3.3/20AS+12/3.3/20AS.optical unit1/3.2 | 48 | ≈1150 | 16.6 | 1055 | 182 | 0.60 | 123 |
| 21 | OPGW-48B1T 50(95; 195) | 1/3.4/40AS+5/3.3/40AS+12/3.3/40AS.optical unit/3.2 | 48 | ≈1150 | 16.6 | 747 | 95 | 0.33 | 195 |
| 22 | OPGW-72B1 -150(172; 110) | 1/3.4/20AS+4/3.3/20AS+12/3.3/20AS.optical unit2/3.2 | 72 | ≈1150 | 16.6 | 998 | 172 | 0.64 | 110 |
| 23 | OPGW-48B1 -170(198; 150) | 1/3.6/20AS+5/3.5/20AS+12/3.5/20AS.optical unit1/3.4 | 48 | ≈1170 | 17.6 | 1190 | 198 | 0.54 | 150 |
| 24 | OPGW-72B1 -170(199; 156) | 1/3.8/20AS+4/3.6/20AS+12/3.6/20AS.optical unit2/3.5 | 72 | ≈1170 | 18.2 | 1187 | 199 | 0.54 | 156 |
| 25 | OPGW-48B1-180(211;175) | 1/3.8/20AS+5/3.6/20AS+2/3.6/20AS.optical unit/3.5 | 48 | ≈1180 | 18.2 | 1255 | 211 | 0.50 | 175 |
| 26 | OPGW-48B1 -180(113;262) | 1/3.8/40AS+5/3.6/40AS+12/3.6/40AS.optical unit/3.5 | 48 | ≈1180 | 18.2 | 888 | 113 | 0.28 | 262 |












