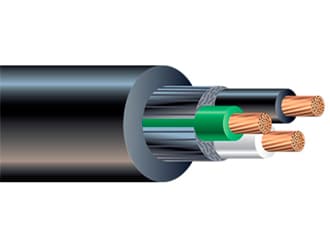
A submersible oil pump cable, also known as ESP (Electric Submersible Pump) cable, is a specialized cable designed to power submersible pumps used in the extraction of oil from underground reservoirs. These cables are engineered to withstand harsh environments, including high temperatures, pressures, and the presence of oil and gas. Submersible oil pump cables are vital components in the oil extraction industry, designed to meet the demanding requirements of deep well operations. Their robust construction, high-temperature, pressure, and chemical resistance, and electrical performance are key factors in ensuring the reliable operation of submersible pumps.
Applications
Oil and Gas Extraction: Primary use in powering electric submersible pumps (ESPs) for lifting crude oil from wells.
Water Wells: Similar technology is applied in water well pumping applications.
Geothermal Wells: Used in geothermal energy extraction, where high temperatures are encountered.
Key Characteristics
High Temperature Resistance: These cables are typically rated to operate in high-temperature conditions, often exceeding 150°C (302°F). This is essential for withstanding the geothermal heat found in oil wells.
Pressure Resistance: Submersible cables must endure high pressures present at great depths. The construction and materials used in the cables are designed to maintain integrity under such conditions.
Chemical Resistance: The cables are exposed to various chemicals, including hydrocarbons and hydrogen sulfide. The materials used, such as specialized rubber or polymer compounds, are selected for their resistance to chemical degradation.
Mechanical Strength: Submersible pump cables are built to be robust and durable, capable of handling the mechanical stresses of installation and operation in deep wells.
Electrical Properties: These cables must provide reliable electrical performance to power the pump motor, which typically operates at high voltage.
Construction
Conductor: Made of copper or aluminum, the conductor must be capable of carrying significant current without excessive heating.
Insulation: High-quality insulation materials, such as EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) or EPR (Ethylene Propylene Rubber), are used to ensure electrical isolation and resistance to high temperatures and chemicals.
Jacket: The outer jacket of the cable provides additional protection against mechanical damage, chemicals, and environmental conditions. Materials like lead sheaths or other advanced polymers are often used.
Armor: In many designs, a layer of armor (often steel) is included to protect against mechanical damage and to enhance the cable’s ability to withstand high pressure and stress.
Temperature Ratings:
Standard, high-temperature, and ultra-high-temperature cables are available to match the thermal conditions of specific wells.
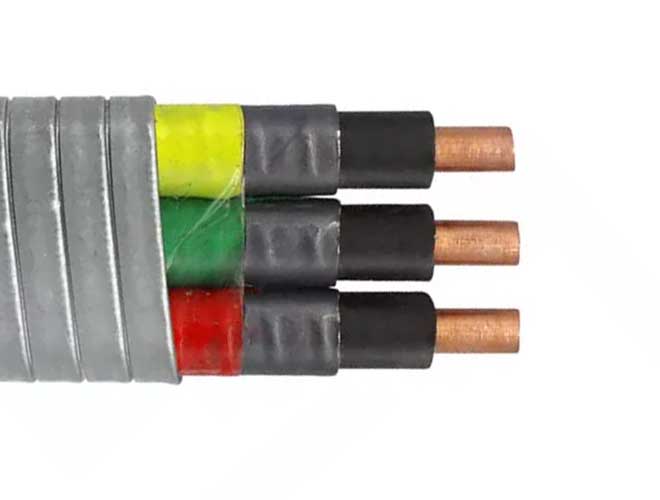
Types of ESP Cables
Round and Flat Cables: Round cables are typically used for deep and deviated wells where flexibility is required.
Flat cables are used where space constraints exist or for certain installation preferences.
3 kV Flat Submersible Oil Pump Cable Parameter
5 kV Flat Submersible Oil Pump Cable Parameter
3 kV Round Submersible Oil Pump Cable Parameter
5 kV Round Submersible Oil Pump Cable Parameter
Installation Considerations
Proper handling and installation are crucial to avoid damage to the cable, which can lead to failures.
The selection of the appropriate cable type and rating is critical to ensure reliable performance and longevity.
Regular monitoring and maintenance are necessary to detect and address any issues arising from the harsh operating conditions.
Get a free quote by E-mail:info@cable-uni.com
Applications
Oil and Gas Extraction: Primary use in powering electric submersible pumps (ESPs) for lifting crude oil from wells.
Water Wells: Similar technology is applied in water well pumping applications.
Geothermal Wells: Used in geothermal energy extraction, where high temperatures are encountered.
Key Characteristics
High Temperature Resistance: These cables are typically rated to operate in high-temperature conditions, often exceeding 150°C (302°F). This is essential for withstanding the geothermal heat found in oil wells.
Pressure Resistance: Submersible cables must endure high pressures present at great depths. The construction and materials used in the cables are designed to maintain integrity under such conditions.
Chemical Resistance: The cables are exposed to various chemicals, including hydrocarbons and hydrogen sulfide. The materials used, such as specialized rubber or polymer compounds, are selected for their resistance to chemical degradation.
Mechanical Strength: Submersible pump cables are built to be robust and durable, capable of handling the mechanical stresses of installation and operation in deep wells.
Electrical Properties: These cables must provide reliable electrical performance to power the pump motor, which typically operates at high voltage.
Construction
Conductor: Made of copper or aluminum, the conductor must be capable of carrying significant current without excessive heating.
Insulation: High-quality insulation materials, such as EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) or EPR (Ethylene Propylene Rubber), are used to ensure electrical isolation and resistance to high temperatures and chemicals.
Jacket: The outer jacket of the cable provides additional protection against mechanical damage, chemicals, and environmental conditions. Materials like lead sheaths or other advanced polymers are often used.
Armor: In many designs, a layer of armor (often steel) is included to protect against mechanical damage and to enhance the cable’s ability to withstand high pressure and stress.
Temperature Ratings:
Standard, high-temperature, and ultra-high-temperature cables are available to match the thermal conditions of specific wells.
Types of ESP Cables
Round and Flat Cables: Round cables are typically used for deep and deviated wells where flexibility is required.
Flat cables are used where space constraints exist or for certain installation preferences.
 |
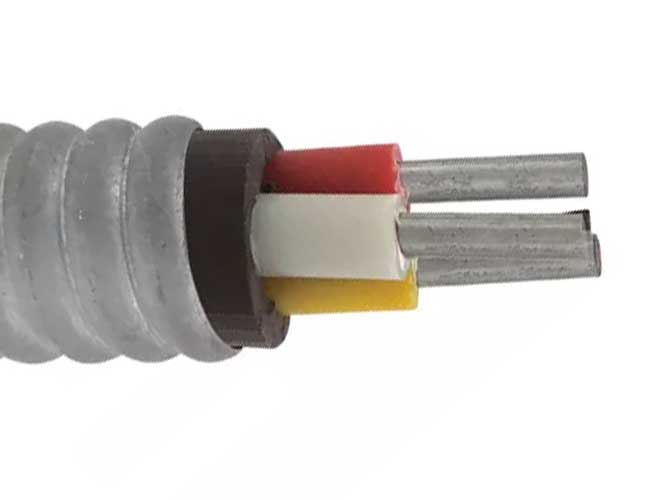 |
3 kV Flat Submersible Oil Pump Cable Parameter
| Conductor Specification | EPDM Insulation | LEAD Sheath | Finished Size ≤ mm | Calculated Weight kg/m | |||||
| AWG | Area m㎡ | Outer Diameter mm | Thickness mm | Outer Diameter mm | Thickness mm | Outer Diameter mm | Thickness mm | Width mm | |
| 6 | 13 | 4.12 | 1.7 | 7.52 | 0.76 | 9.12 | 13.14 | 35.72 | 1.7 |
| 4 | 20 | 5.19 | 1.7 | 8.59 | 0.76 | 10.19 | 14.21 | 35.93 | 2.1 |
| 2 | 33 | 6.54 | 1.7 | 9.94 | 0.76 | 11.54 | 15.56 | 40.00 | 2.6 |
| 1 | 42 | 7.35 | 1.7 | 10.75 | 0.76 | 12.35 | 16.37 | 42.41 | 3.0 |
| Conductor Specification | EPDM Insulation | LEAD Sheath | Finished Size ≤ mm | Calculated Weight kg/m | |||||
| AWG | Area m㎡ | Outer Diameter mm | Thickness mm | Outer Diameter mm | Thickness mm | Outer Diameter mm | Thickness mm | Width mm | |
| 6 | 13 | 4.12 | 1.9 | 7.92 | 0.76 | 9.52 | 12.54 | 34.00 | 1.85 |
| 4 | 20 | 5.19 | 1.9 | 8.99 | 0.76 | 10.59 | 14.61 | 37.13 | 2.23 |
| 2 | 33 | 6.54 | 1.9 | 10.34 | 0.76 | 11.94 | 15.96 | 41.00 | 2.77 |
| 1 | 42 | 7.35 | 1.9 | 11.15 | 0.76 | 14.75 | 16.80 | 43.60 | 3.14 |
| Conductor Specification | EPDM Insulation | LEAD Sheath | EPDM Shealth | Finished Size ≤ mm | Calculated Weight kg/m | |||||
| AWG | Area m㎡ | Outer Diameter mm | Thickness mm | Outer Diameter mm | Thickness mm | Outer Diameter mm | Thickness mm | Outer Diameter mm | ||
| 6 | 13 | 4.12 | 1.7 | 7.92 | 0.75 | 9.12 | 1.52 | 23.71 | 28.61 | 2.03 |
| 4 | 20 | 5.19 | 1.7 | 8.99 | 0.75 | 10.19 | 1.52 | 26.01 | 30.92 | 2.44 |
| 2 | 33 | 6.54 | 1.7 | 10.34 | 0.75 | 11.54 | 1.52 | 28.92 | 33.82 | 3.02 |
| 1 | 42 | 7.35 | 1.7 | 11.15 | 0.75 | 12.35 | 1.52 | 30.66 | 35.57 | 3.40 |
| Conductor Specification | EPDM Insulation | LEAD Sheath | EPDM Shealth | Finished Size ≤ mm | Calculated Weight kg/m | |||||
| AWG | Area m㎡ | Outer Diameter mm | Thickness mm | Outer Diameter mm | Thickness mm | Outer Diameter mm | Thickness mm | Outer Diameter mm | ||
| 6 | 13 | 4.12 | 1.9 | 7.92 | 0.75 | 9.52 | 1.52 | 24.57 | 30.50 | 2.12 |
| 4 | 20 | 5.19 | 1.9 | 8.99 | 0.75 | 10.59 | 1.52 | 26.81 | 32.78 | 2.59 |
| 2 | 33 | 6.54 | 1.9 | 10.34 | 0.75 | 11.94 | 1.52 | 29.78 | 35.70 | 3.11 |
| 1 | 42 | 7.35 | 1.9 | 11.15 | 0.75 | 12.75 | 1.52 | 31.53 | 37.43 | 3.50 |
Installation Considerations
Proper handling and installation are crucial to avoid damage to the cable, which can lead to failures.
The selection of the appropriate cable type and rating is critical to ensure reliable performance and longevity.
Regular monitoring and maintenance are necessary to detect and address any issues arising from the harsh operating conditions.
Get a free quote by E-mail:info@cable-uni.com


SSHÖU3E.png)